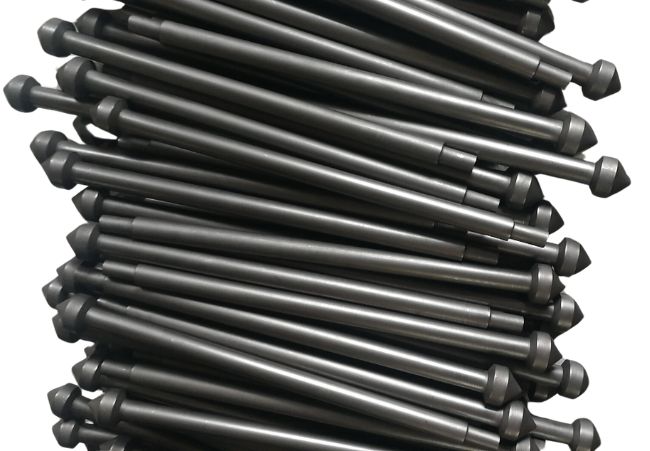
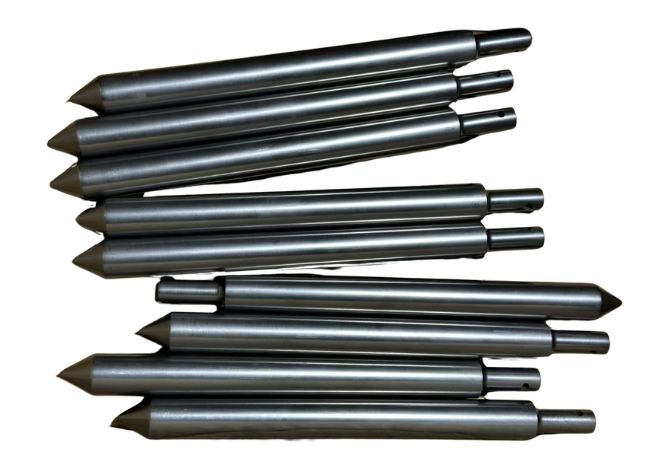
Polished Graphite Rods
Polished graphite rods are finely processed graphite products with unique physical and chemical properties that are widely used in many industrial fields.
1 High purity and density
Polished surface, smooth and non-porous, extremely low impurity content, high chemical stability, resistant to acid and alkali corrosion.
2 Excellent high temperature resistance
Can operate at high temperatures (above 3000°C in a non-oxidizing environment), has a low thermal expansion coefficient, and good thermal shock resistance.
3 Excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity
With electrical conductivity close to that of metals and excellent thermal conductivity, it is suitable for applications requiring rapid heat transfer.
4 Self-lubricating properties
Graphite has weak interlayer bonding and low friction coefficients, reducing mechanical wear without the need for additional lubricants.
What Types of Graphite Rods does CD Graphite Company Have?
CD Graphite Company’s graphite rods cover almost all types, such as isostatic polished graphite rods, vibrated graphite rods, molded graphite rods, extruded graphite rods, etc., classified by graphite molding material; there are also graphite rods with various coatings, purified graphite rods, etc.
Stable conductivity at 3000°C in a furnace, and reliable operation in highly corrosive environments. CD Graphite Company’s graphite rods, utilizing advanced graphite material technology, provide high-temperature resistant, highly conductive, and ultra-stable solutions for your core processes.
Isostatic Graphite Rod
Isostatic graphite rods are graphite rods machined by isostatic graphite. They inherit the core advantages of isostatic graphite, and due to their specific rod-shaped form, exhibit some distinctive characteristics in terms of performance and application.
For example, they exhibit high isotropy. Physical properties such as strength, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and thermal expansion are highly uniform along both the axial (lengthwise) and radial (diameter) directions, with no directional differences. Compared to traditional extruded graphite rods (which exhibit significant anisotropy in performance), they are more suitable for applications requiring uniform performance in multiple directions.
High density and low porosity. The density is typically ≥1.75 g/cm³ (high-end products can reach 1.85-1.90 g/cm³), with a dense structure and low porosity (<15%), reducing the risk of gas permeation and oxidation.
Excellent mechanical strength. High flexural strength (≥40 MPa) and compressive strength (≥80 MPa), maintaining stability at high temperatures without deformation or fracture.
Excellent thermal performance. High thermal conductivity (70–120 W/m·K): Rapid and uniform heat transfer, preventing localized overheating. Low thermal expansion coefficient (4–6×10⁻⁶/K): Minimal thermal deformation, excellent thermal shock resistance, capable of withstanding rapid cooling and heating cycles (e.g., high-temperature to cooling cycles in semiconductor processes).
High purity and chemical stability. Ash content can be less than 5 ppm (semiconductor grade), avoiding contamination of sensitive processes. Resistant to acid and alkali corrosion (except strong oxidizing acids), suitable for corrosive environments.
Vibrated Graphite Rod
Vibrated graphite rod is graphite rod machined by vibrated graphite block. Therefore, it possesses the physical and chemical properties of vibrated graphite raw material blocks.Its particle size is not as fine as isostatic graphite and molded graphite, and is approximately 0.8 mm or 2 mm, or even coarser. The density we commonly use is approximately 1.72 g/cm³ and 1.68 g/cm³ or higher. Therefore, compared to isostatic and molded graphite, vibrated graphite rods are very cost-effective. In addition, vibrated graphite has a very low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent dimensional stability at high temperatures.Anywhere that requires precise shape, position, or sealing under changing temperatures requires the low thermal expansion coefficient characteristic of graphite.

Molded Graphite Rod
Molded graphite rodis graphite rods machined by molded graphite block. Its material is cheaper than isostatic graphite, because the process for molded graphite blocks is simple and requires little investment in equipment.However, it has its own advantages, such as high compressive/flexural strength along the pressure direction.It can be used in areas where uniformity is not a high priority, such as brushes, ordinary electrodes, and mechanical seal rings, ordinary electric spark machining electrodes and heating elements in heat treatment furnaces and so on.
Isostatic graphite, with its near-perfect uniformity and stability, has become the “material ceiling” for high-end industries; molded graphite, on the other hand, meets basic requirements with its cost-effectiveness, and the two complement each other in terms of positioning.
Extruded Graphite Rod


Whether it is isostatic graphite rods, vibrated graphite rods, or molded graphite rods, they are all machined by raw materials into graphite rods. Unlike the above types of graphite rods, extruded graphite rods are directly extruded into round shape using equipment.
High thermal conductivity: Axial thermal conductivity as high as 120-150 W/(m·K), more than three times that of metals, making it suitable for heat dissipation applications.
Low thermal expansion coefficient: Thermal expansion coefficient (1~4×10⁻⁶/K) is close to that of quartz glass, providing excellent thermal shock resistance.
Good electrical conductivity and extremely low resistivity: Resistivity is approximately 8 to 15 μΩ·m, making it suitable for use as an electrode material.
Machinability: It can be machined into complex components (such as crucibles and heating elements) through turning and drilling, but it has high brittleness and must be protected from impact.












